Image: "Coarctation of the Aorta" by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is in the public domain. Link to the source.
Coarctation of the aorta
Jump to content
Definition Aetiology Pathophysiology Risk factor Sign and Symptoms Investigations Management
Definition
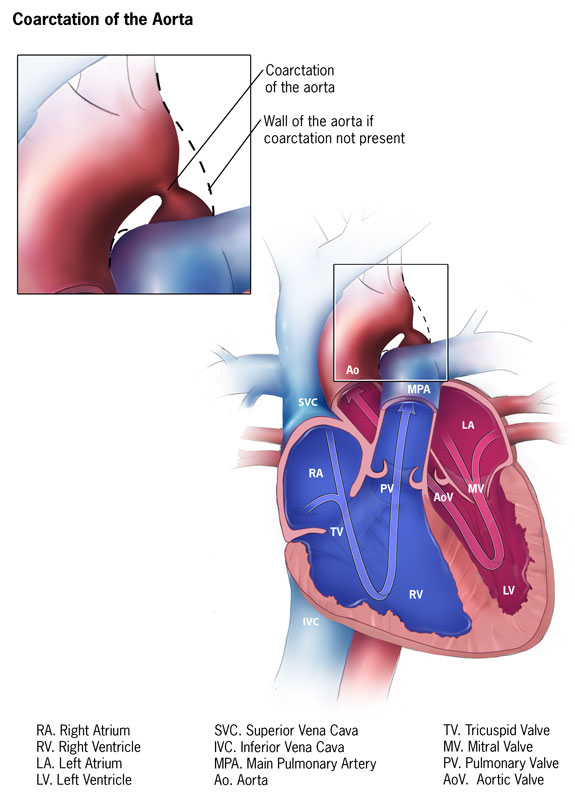
A congenital heart condition in which the aorta is constricted. The aorta is the main organ transporting oxygenated blood from the heart to the body.
Aetiology
Combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Pathophysiology
Flow of blood to the body is reduced because the aorta has become constricted. In addition, there is increased pressure in the upper part of the body and reduced pressure in the lower part of the body.
Risk factors
Family history of congenital heart defects.
Maternal hypertension during pregnancy.
Some genetic disorders.
Sign and symptoms
Pale skin.
Difficulty breathing/ feeding.
Perfused sweating.
O/E: radio-femoral delay +/- weak femoral pulse.
Systolic murmur on L infraclavicular area and below Left scapula.
Investigations
Physical examination.
Chest X-ray: may show signs of heart failure or shadowing at the coarctation site.
Cardiac MRI.
Electrocardiogram (ECG).
Echocardiogram.
Management
Anti-hypertensive medications (ACEi, Beta-blockers, CCB)
Surgery ( balloon angioplasty)
Check out our youtube channel
Blueprint Page
Explore the comprehensive blueprint for Physician Associates, covering all essential topics and resources.
Book Your Session
Enhance your skills with personalised tutoring sessions tailored for Physician Associates.

