Cardiac Tamponade
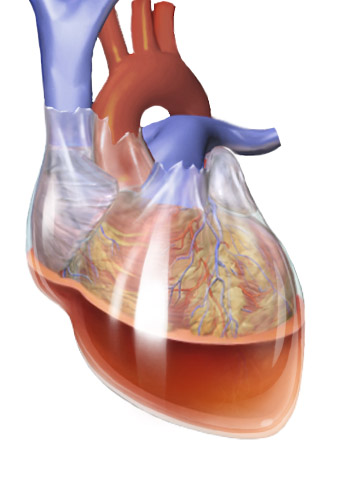
This illustration shows cardiac tamponade, a condition where the pericardium becomes filled with blood (hemopericardium), compressing the heart and impairing its function.
Image by BruceBlaus, licensed under CC BY 3.0. Cited from: Blausen.com staff (2014). "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine, 1(2). DOI: 10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436.
Definition
Cardiac tamponade is a medical condition in which fluid accumulates in the pericardial space surrounding the heart. This is a medical emergency because the heart is experiencing increased pressure as a result of build or build. Without treatment, cardiac tamponade can be fatal.
Aetiology
Acute causes:
Chest trauma/injury
Idiopathic (no known causes)
Myocardial infarction (MI)
Pericarditis
Heart surgery generally caused by a post-surgical complications
Chronic causes:
Cancer.
CKD related uremia
Connective tissue disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and Lupus.
Tuberculosis (TB): a complication from TB.
Pathophysiology
The accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space raises the heart's intracardiac pressure, impairing its ability to pump blood. Additionally, there is a decrease in blood flow through the heart.
Risk factors
Pericarditis: Individuals with a history of previous pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium)
Cancer
Heart failure
Kidney failure
Radiation therapy: radiation therapy performed around the heart area
Sign and symptoms
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Tachycardia
Tachypnoea
Weakness
Dizziness
Investigations
Diagnosis starts with a physical examination of the patient and a good history.
Investigations may include:
ECG
CXR - fluid in the pericardial space can be observed
ECHO
CT SCAN
MRI
Cardiac catheterisation
Culture of fluid from a pericardiocentesis
Management
Medical emergency - patient must be admitted to the hospital
Pericardiocentesis: drainage of fluid in the pericardial space through a needle or a catheter inserted through the chest into the pericardial space.
Treat underlying causes such as TB, pericarditis, MI etc.
